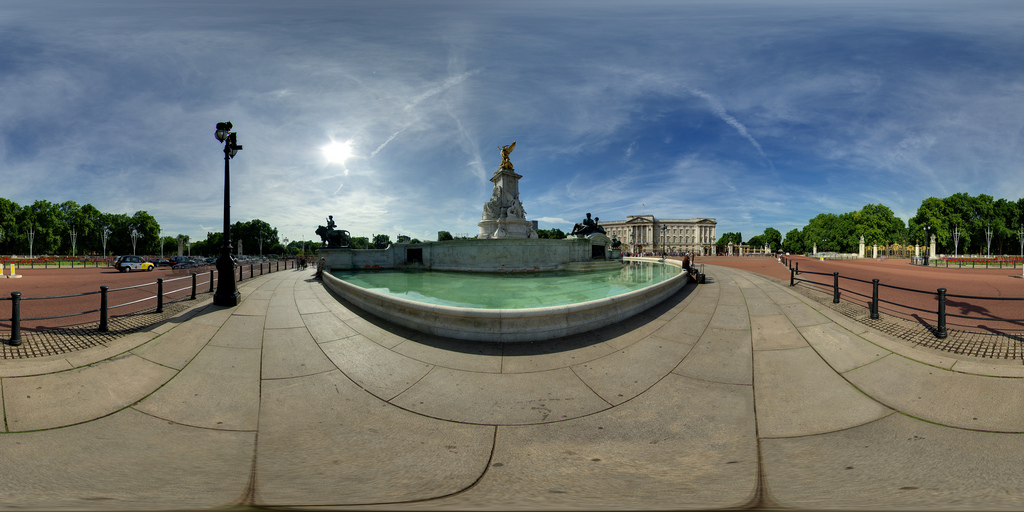
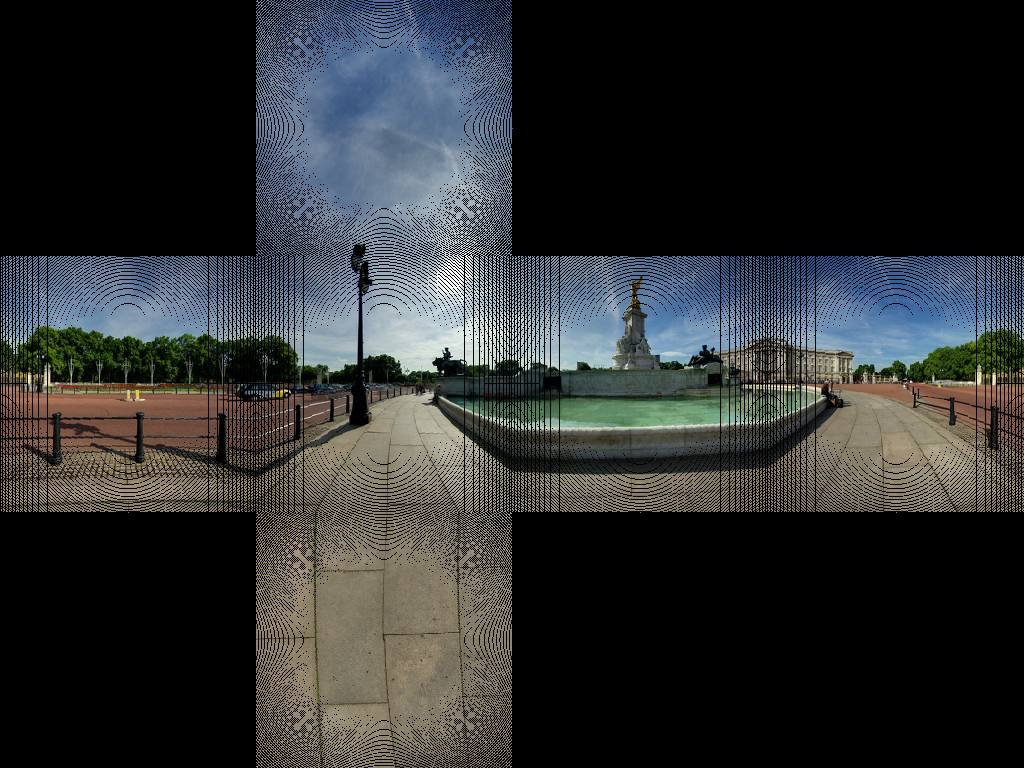
(译)stackoverflow上关于柱形全景与立方体全景转换的讨论
提问:
@ WestLangley:
我正在给某网站开发一个简单的3D全景浏览功能。考虑到移动端的性能,我使用了three.js的CSS3 renderer。它需要一个由六张图组成功立方体贴图。
我用iPhone上的“Google Photosphere”(或其他类似的app)创建了一个2:1的柱形全景图,然后用这个网站(需要Flash)把柱形全景图转换成了立方体全景图。
但是我想自己完成这种转换,比如用three.js或者Photoshop。我发现Andrew Hazelden’s好像用Photoshop做过类似的操作,但是没有那种直接转换的。有没有什么数学方法或者现成的js库可以做到的?尽量不要使用Blender这类3D软件来做。
也许实现会比较复杂,但是还是打算来问一下。本人js基础还阔以,但是用three.js没多久,因为WebGL在移动端好像跑起来有点慢,兼容性也一般,所以犹豫要不要用它的函数库。
提问下的回复:
@ Salix alba:可以通过在js中使用CSS或canvas做到,但是我不确定three.js是不是也可行:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/8912917/cutting-an-image-into-pieces-through-javascript
@ Eric Seifert: 我用一段python代码实现了:https://github.com/seiferteric/cubemap
最高票回答:
@ Salix alba
如果是要在服务端做的话选项有很多。http://www.imagemagick.org/里有一堆命令行工具可以对图片进行切割,你可以把这些命令放到你的代码里面,每次要转换的时候就执行。
很难说清楚这些命令里面用了哪些算法。我们可以通过一张正方形网格图片看看程序做了什么操作(译者注:有点拗口不好翻,大概就这意思)。我用维基上的一张网格图来示例。
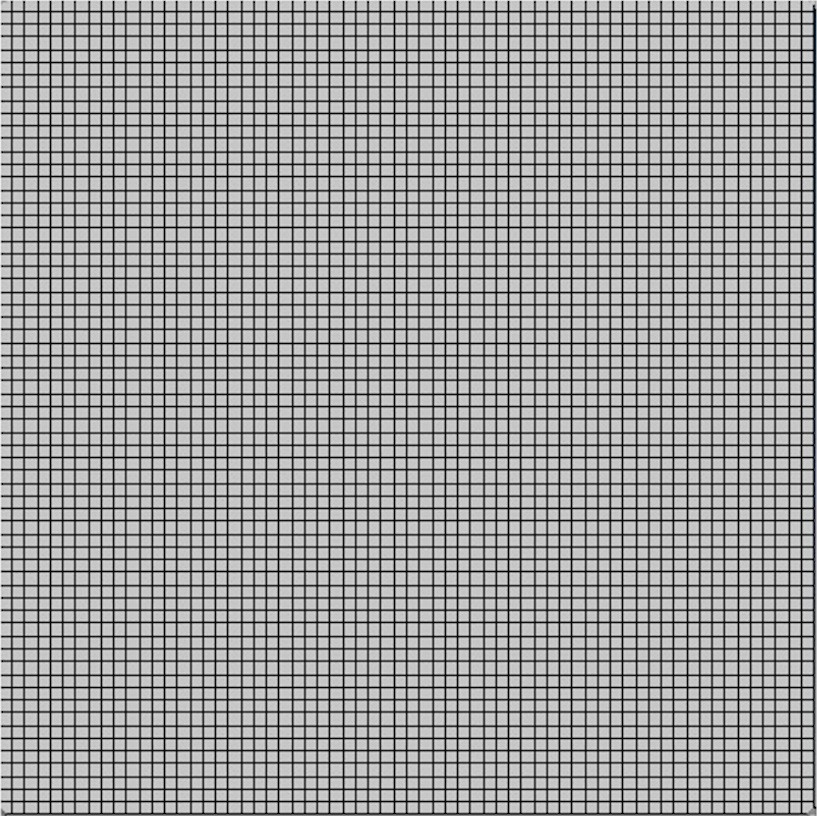
转换后
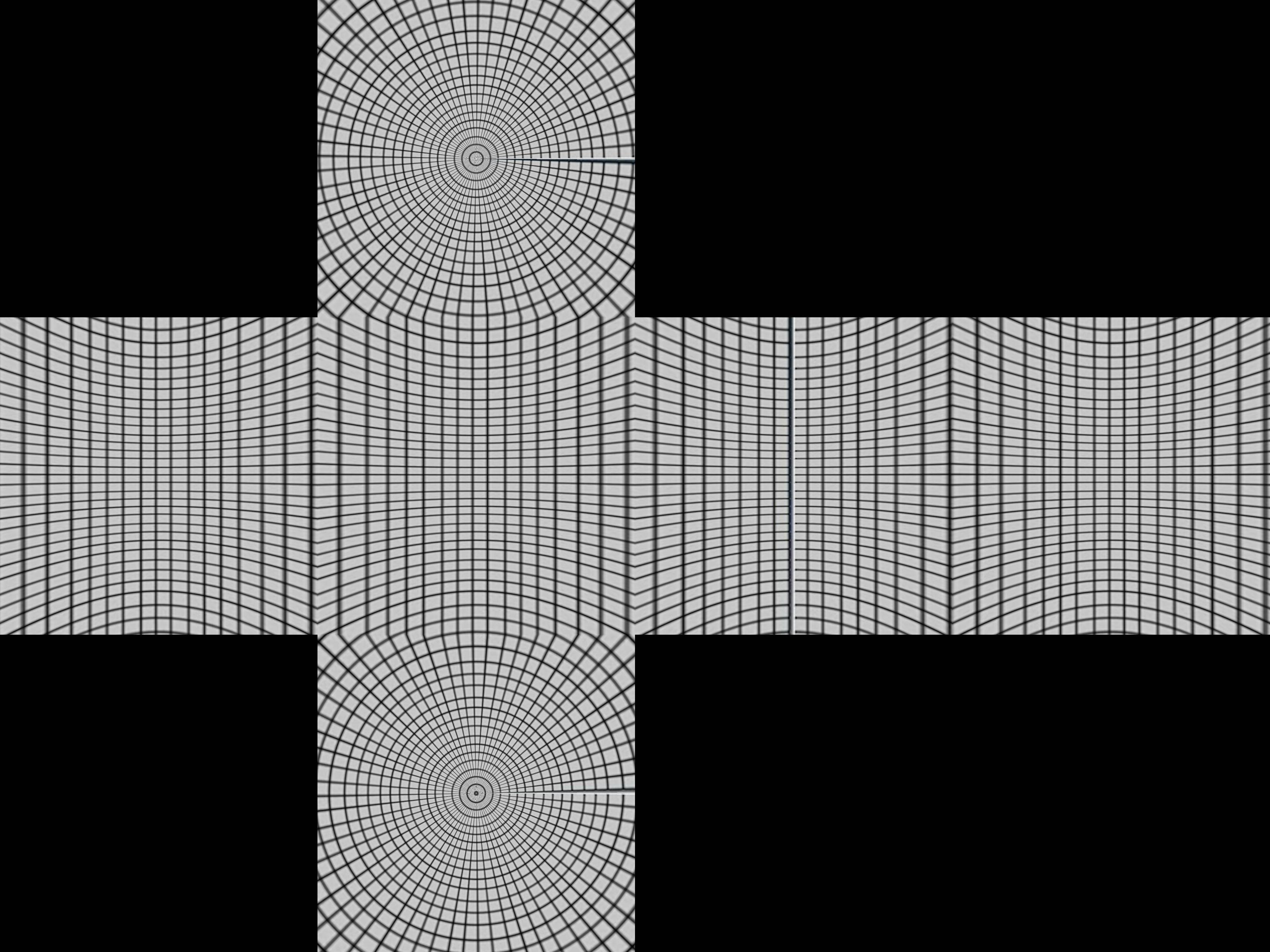
通过这两张图可以看出立方体映射是如何映射的。
想象一下,有一个布满经纬线的球体被一个立方体包裹,然后从球的中心点投影到立方体上,产生一个扭曲的网格。
用数学来说明,有极坐标r,θ,ø,球半径 r = 1。 0 <θ<π,-π/4<ø<7π/ 4
x= r · sinθ · cosø
y= r · sinθ · sinø
z= r · cosθ
要把它们映射到立方体上,首先我们通过纬度范围 -π/4 < ø < π/4, π/4 < ø < 3π/4, 3π/4 < ø < 5π/4, 5π/4 < ø < 7π/4 将球体分成四个区块,它们会被投射到每个面的顶部或底部。
假设我们在第一个面(-π/4 < ø < π/4),sinθ · cos ø、sinθ · sin ø、cosθ 经过 中心投影到x=1的平面上后会变成a · sinθ · cosø、a · sinθ · sinø、a · cosθ。
因为 a·sinθ · cos ø = 1,所以 a = 1 / (sinθ · cosø)
因此投影后的点坐标为(1, tanø, cotθ / cosø)
如果 | cot θ / cos ø | < 1,这个坐标点会位于正面,否则就会出现在上面或下面,这时你就要使用另一套方法来计算投影。因为cosø最小值 = cosπ/ 4 = 1 / √2,所以如果cotθ/(1 /√2)>1或tanθ<1 / √2,投影点坐标一定是在上面。结果是θ<35º或0.615弧度
把上面的推算过程用python实现:
1 | import sys |
projection函数接收theta和phi两个参数并返回其投影在球体上的坐标(范围是-1~1)。
cubeToImg函数接收一个包含xyz坐标的元组和立方体边长输出到图片坐标系中
网上找了一张全景图,用上面的算法对其进行转换以后,得到了正确的形状:
好像只有大部分的线是铺对的,又一部分图像没有任何像素,这是因为像素投影没有一 一对应,我们需要再做一次逆转换。先在源图像上遍历每个像素,然后在目标图像上找到每个对应的点。接着遍历目标图像,在对应的原图像上找到最近的像素。
修改代码后:
1 | import sys |
重新生成后的结果:
英文好的可以看原文:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29678510/convert-21-equirectangular-panorama-to-cube-map,有翻译上的问题欢迎指出。
后面的回复还有不少干货,有空我会继续翻译


